Lower capital G-SIB requirements loom for Chinese megabanks amidst shadow banking crackdown
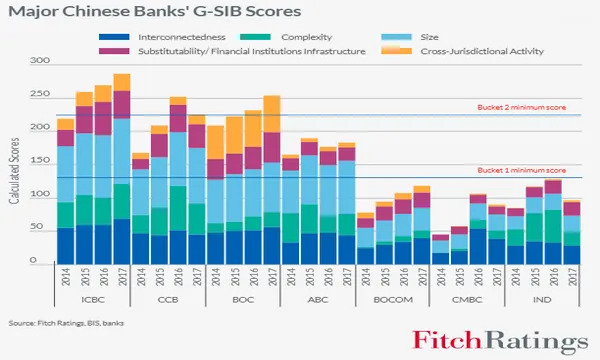
CCB’s extra CET1 requirements fell to 1% from 1.5%.
China’s ongoing crackdown to curb risk in the financial services sector and cut down on banking interconnectedness and complexity comes as a boost to the country’s megabanks who have to shell out less in capital requirements as they skirt away from being tagged as global systemically important banks (G-SIBS), according to Fitch Ratings.
Released by the Financial Stability Board, the list of G-SIBS are set as an additional safeguard against market shocks, a legacy of the 2008 crisis. G-SIB status obliges extremely large banks to meet extra CET1 requirements which range from 1.0% to 3.5%. This year’s list features JP Morgan Chase in the fourth bucket with an additional capital buffer of 2.5% whilst Citigroup, Deutsche and HSBC could be found in the third bucket with an additional 2% capital requirement.
Also read: China dominates world's largest banks even as Europe flexes financial muscle
Chinese G-SIBS will be required to maintain minimum total loss-absorbing capacity (TLAC) requirements of 16% of risk-weighted assets by January 1, 2025 and 18% by 2028, assuming no acceleration.
“Increased capital requirements should benefit banks' Viability Ratings, provided additional buffers are not eroded by greater risk appetite,” the firm said in a report.
China Construction Bank (CCB) was also moved into a lower G-SIB bucket 2 which entails less extra common-equity Tier 1 (CET1) requirements. CCB will now be subject to an additional 1.0% CET1 buffer from 1.5%.
The G-SIB scores of mid-tier banks China Minsheng Banking Corporation (CMBC) and Industrial Bank (IND) also fell significantly on the back of lower sub-scores for interconnectedness and complexity, which puts them a farther position from triggering the minimum G-SIB threshold.
Also read: Chinese banks are the world's sixth largest creditor group
However, Bank of Communications (BOCOM) is still likely to be designated as a G-SIB within the next two years provided that growth and interconnectedness levels are maintained. Its G-SIB score is likely to approach the “bucket 1” threshold in the next two years as it continues to grow in size.
“We also think CCB can easily move back into "bucket 2" as it continues to build scale domestically and internationally. This suggests the drop in its minimum capital requirements during this review may be temporary,” the report’s authors added.




![Lorem Ipsum [ABF 1]](https://cmg-qa.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/styles/exclusive_featured_article/public/2025-03/a_hand_pointing_to_a_futuristic_technology_5b87c9d0e3_1.png.webp?itok=2w0y1WhS)


![Cross Domain [Manu + SBR + ABF + ABR + FMCG + HBR + ]](https://cmg-qa.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/styles/exclusive_featured_article/public/2025-01/earth-3537401_1920_4.jpg.webp?itok=WaRpTJwE)





 Advertise
Advertise

